Azure Automation with Managed Identity enables you to automate and orchestrate various tasks and processes within Azure environments. With the added benefit of Managed Identity, it eliminates the need for using credentials and simplifies authentication and authorization process.
By leveraging Azure Automation, you can create and schedule runbooks, which are sets of instructions or scripts, to perform routine or complex operations such as provisioning resources, managing virtual machines, or deploying applications. These runbooks can be executed on a schedule or triggered by specific events.
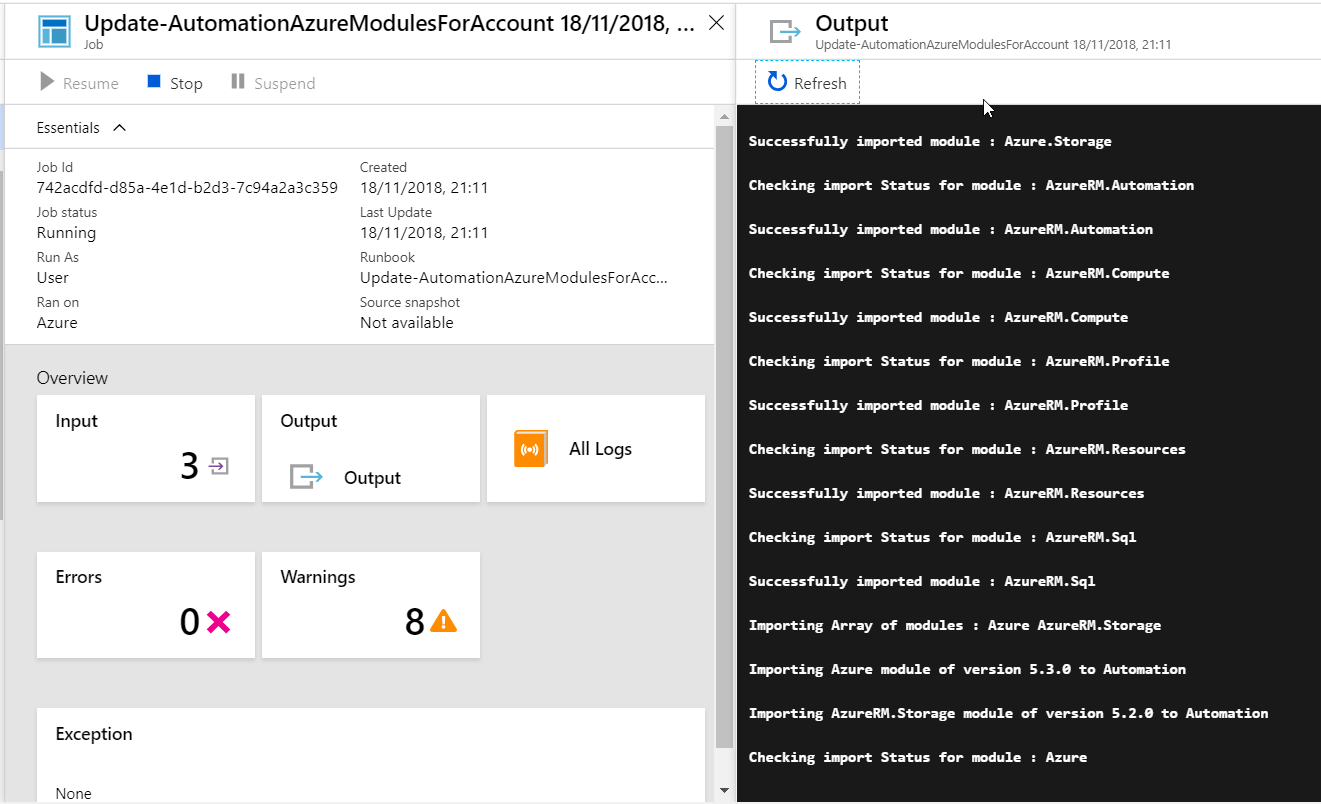
In this post we will go through setting in an Azure Automation account, runbook and use a managed identity to authentication.
To create a automation account.
Go to the Automation Account blade and click create.

Set the subscription, resource group, name and region.

Set the managed identities, we will be using system assigned the below link to Microsoft document outlines the differences between system / User.

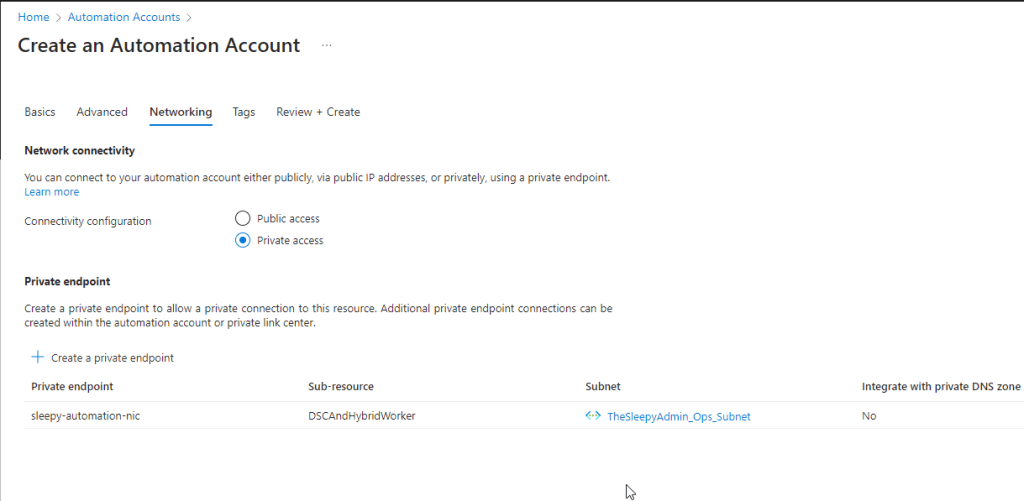
We will be setting connectivity configuration to private access and create a private endpoint to assign a NIC with a private IP.
Next set tags if required.
Review the details and deploy.

It will take a minute or so for the deployment to complete.

We can now check and confirm that the service principal for the automation account has been created.
We can check by going to to Azure AD > Enterprise Application and search with the objectID

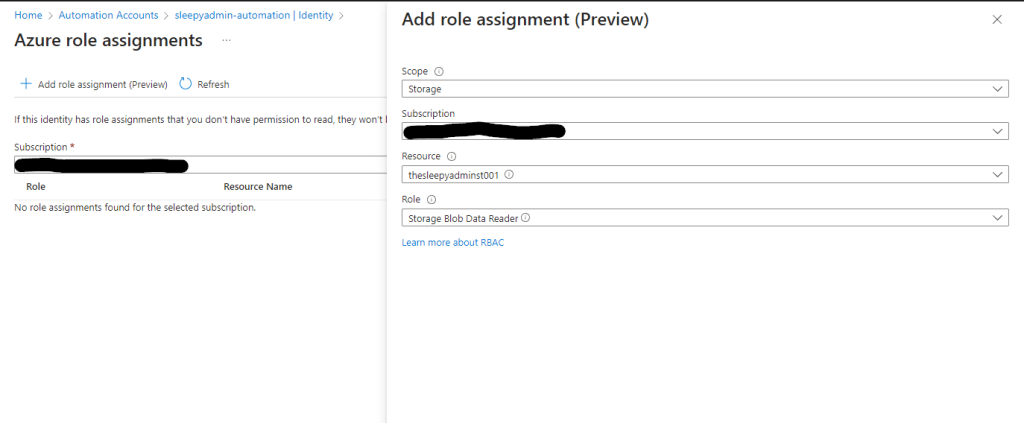
Next we need to assign the required permission. To assign go to Identity and select Azure role assignments.

The permission can be scoped to subscription, resource group, key vault, storage account. I will be setting scope to storage and assigned the storage blob data reader to one of my storage accounts.
Save and the role should apply.

Next we will create a runbook to run a set of task using the managed identity of the automation account.

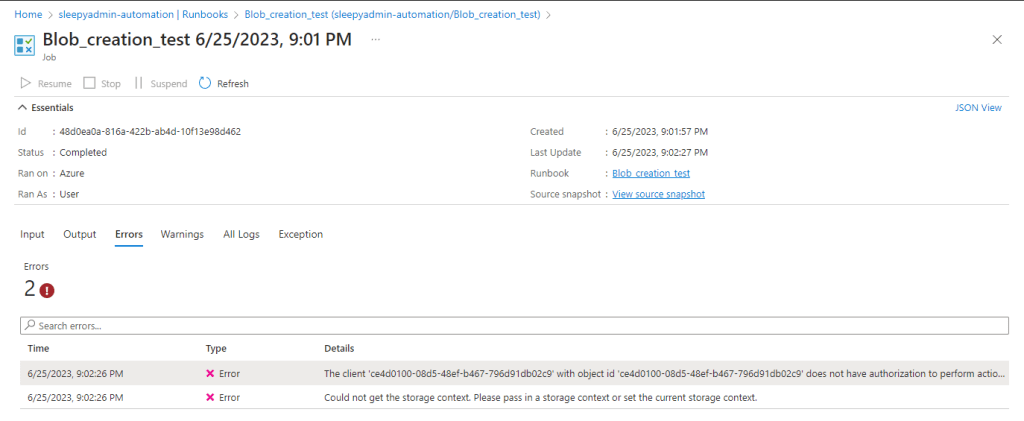
Add in the PowerShell script to be run. I am going to try create a blob container but this should fail as I have only give read access. Click publish to allow the runbook to be run.

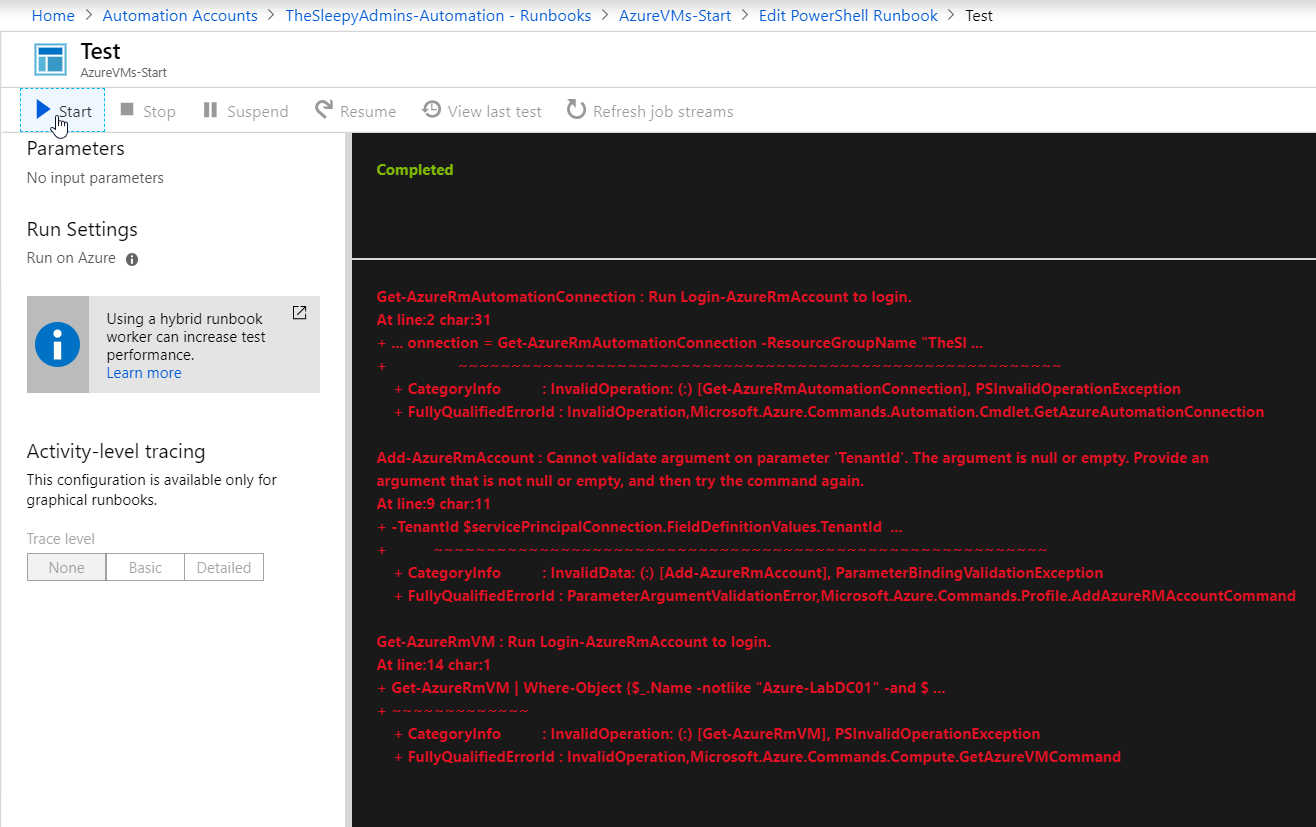
Click start to run the runbook.

Once competed we can view the errors from the run.
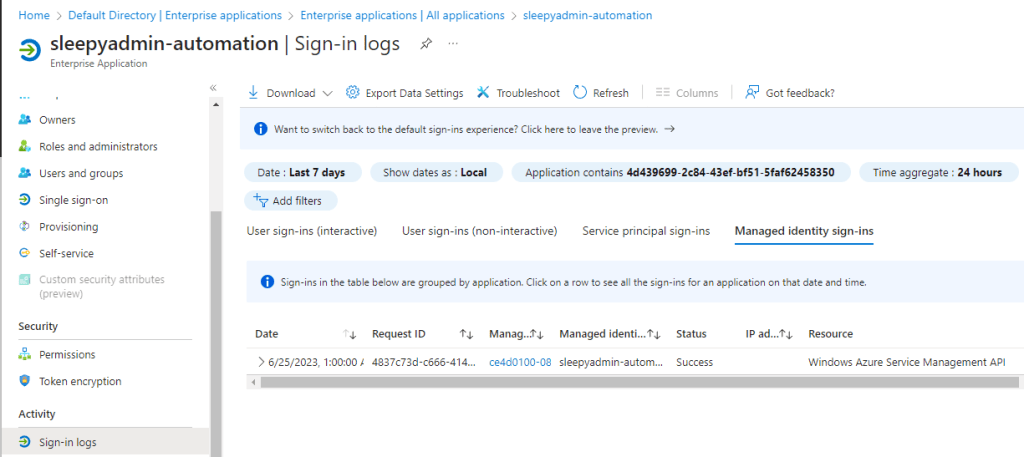
We can also check the enterprise app for the automation account and see the sign-in was successful.
This was just a quick example Azure Automation with Managed identify, this can be a very useful tool for setting up task that need to be run on a scheduled in Azure.